As the digital landscape continues to evolve, email is becoming increasingly important for businesses and organizations. Email accounts are essential for most organizations, allowing them to communicate with customers, suppliers, and colleagues. As a result, it is important to ensure that emails are validated and secure. This is especially true in the age of data privacy and security regulations. Validated email addresses provide many benefits to businesses, including improved customer experience, better customer service, stronger data security, and most importantly, improved email deliverability.
Most businesses and individuals have had to deal with email bounces or spam reports. That happens because outbound emails can bounce or risk a spam complaint if the email is sent to an invalid, inactive or non-existent email address. Most of the time, the sender is unaware of this error and resends the email to the recipient, repeating the same mistake over and over again, and making a bad situation even worse.
Email validation is one of the most important steps in ensuring your email communication's accuracy, security, and efficiency. It is a widely used tool employed by various players in the online world--from marketers and email list brokers to web admins and website owners. But many people don't understand what email validation is or how it works. Validating email addresses can help companies, marketers, and website owners ensure that their email communications reach real people without bouncing or ending up in spam folders.
This blog post will explore the basics of email validation, including how it works, its purpose, the benefits it offers, and the different types of validation tools available. We will also discuss how to ensure your emails are validated correctly and the best practices to follow when validating emails. By the end of this blog post, you will better understand email validation and how to use it to keep your email communication secure and efficient.
Introduction: What is Email Validation?
Email validation is a process that checks an email address for legitimacy, accuracy, and authenticity in real time. It can be done manually by sending an email to the address and receiving a reply or verifying that the email address exits and is authentic through an automated system such as an email verification service. Generally, email validation involves checking if the email address exists and is valid from a technical point of view and if it is still active and can receive messages.
The process of email validation is incredibly important for businesses, as it helps protect them from sending marketing messages to invalid or inactive email addresses, which can lead to a high bounce rate, wasted resources, and a loss of potential customers. This process aims to ensure that the sender's address is accurate and not fraudulent in any way. It helps businesses ensure that their email marketing campaigns reach the right people and that the information they have collected is accurate and up to date.
Whether you are sending emails to prospects, clients, or other stakeholders, email validation is an important part of a successful email marketing strategy. It helps to protect your business from email deliverability issues, spam traps, and malicious attacks. It involves verifying the syntax, domain, MX records, and mailbox of an email address to determine if the email address exists or is valid and can be used to send and receive messages. It helps to protect businesses and organizations from potential spam, phishing, spoofing, and fraud attempts by verifying the validity of email addresses before they are added to a mailing list.
Some Email Terminologies and Their Meanings
1. Email Bounce:
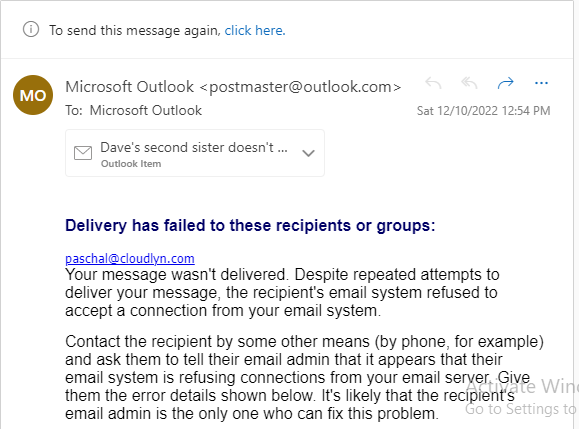
An email bounce is a delivery issue that occurs when an email cannot reach its intended recipient. This can be due to a number of causes, such as the recipient's email account being disabled or deleted, the recipient's mailbox being full, the recipient's address being incorrect, or the recipient's server rejecting the message due to suspicion of spam or malware. Email bounces are often identified by an error message or bounce code. Typically, the sender will receive a "bounceback" notification carrying the bounce codes that explain the cause of the bounce.
Email bounces can occur for a variety of other reasons. For instance, if the email contains an attachment that is too large for the recipient's server, or if the sender's server is down due to technical difficulties or maintenance, or if the recipient's server is rejecting emails from the sender due to spam filtering, virus protection program or other security measures. In some cases, email bounces are caused by misconfigurations or errors in the sender's email account or server settings, such as incorrect authentication or invalid domain name settings. In any of these cases, a sender may need to contact the recipient's server administrator to identify and resolve the issue.
Email bounces can be divided into hard bounces and soft bounces.
a) Hard Bounce:
A hard bounce is an email delivery status that indicates a permanent delivery failure and prevents the recipient from receiving the message. This is one of two types of bounce, the other being a soft bounce, which is a temporary delivery failure. Hard bounces are commonly triggered by an invalid or non-existent email address, an inactive domain name, or when the server hosting the email address has permanently rejected the message due to content restrictions or other reasons.
When an email hard bounces, the sender should remove the recipient from their list and address the issue to ensure any future emails can be delivered successfully. It is important to note that any messages that hard bounce should not be resent, as the email address could be invalid, and the message will never be delivered. It is vital to monitor hard bounces when sending emails, as they can indicate that your lists of email addresses are outdated or there are technical issues with your email server.
b) Soft Bounce
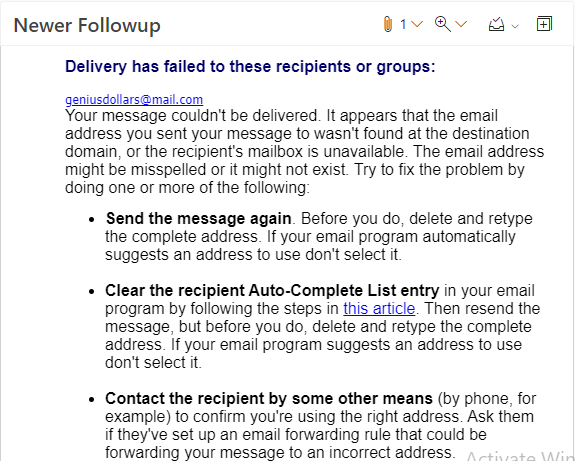
A soft bounce is a type of email bounceback that occurs when the recipient's email server temporarily rejects the message. Unlike a hard bounce, which is an email delivery failure caused by an invalid or non-existent address, a soft bounce is usually an indication of a temporary problem.
Common causes of soft bounces include a full inbox, a server that is down, or a message that is too large. Soft bounces can also be caused by an authentication issue, such as a recipient's mail server rejecting the sender's address. While the message is temporarily rejected, the sender can often retry sending it at a later time. If the issue persists, it may be necessary to contact the recipient's mail server administrator to resolve the issue. However, if soft bounces continue to occur, the sender should review their mailing list and clean out any invalid or non-existent email addresses.
2. Inactive Email:
An inactive email address is an email address that is no longer receiving or sending messages or a mailbox that has not been used for an extended period. This type of email address is often referred to as a dormant or abandoned email address. Inactive email addresses are generally the result of a user not logging into their account for a long period of time, or simply because they no longer use the address.
For the most part, inactive email addresses still exist; however, they are no longer actively monitored or used. It could be an address that was set up and then forgotten, or it could be an address that is no longer in use due to the user transitioning to a new email service. Inactive email addresses are common, as users often forget to keep up with their email accounts or find that they no longer need the address they had set up.
Inactive email addresses can cause various issues, from cluttering up databases to causing confusion when attempting to contact someone. They can be problematic from a business perspective, as they can lead to communication issues and potential security risks. It is important to periodically review email databases to ensure that all inactive email addresses are removed or identified as such. Businesses should be aware of any inactive email addresses in their contacts list and take steps to ensure that their communications are securely sent to active accounts.
3. Spam trap Email:
A spam trap is an important tool for businesses and organizations to protect their networks from malicious campaigns and their customers from exposure to malicious communications.
A spam trap email is a type of email address used to detect and block email messages sent by spammers and other malicious actors. It is designed to detect and identify malicious emails, such as those containing malicious links or attachments, which are sent with the intent to compromise a user’s security. This type of email address is made up of a hidden address that is invisible to the sender and is often used by email providers to test for spam.
When a malicious email is sent to a spam trap address, it is flagged as suspicious and blocked from reaching its intended recipient. This helps protect users from potentially dangerous emails and can also be used to help identify the sender of the malicious email. This can help in the prevention of spam propagation.
These addresses are often created and managed by anti-spam organizations, internet service providers, and email service providers to identify and block the deceptive campaigns designed to get around traditional anti-spam measures. The email messages these addresses receive are monitored and analyzed, and any suspicious emails are blocked, preventing them from reaching legitimate recipients.
Spam-trap email addresses are typically not used by real people; they are used to identify spammers by monitoring for incoming emails sent to these addresses. Any emails sent to these addresses are considered unsolicited and are flagged as spam. Spam traps can also be found in public databases, such as those containing email addresses from past customers or from websites that scrape emails from other sources.
These spam emails are important to identify and block because they can both negatively impact a sender's reputation, as well as lead to higher levels of spam in the overall ecosystem. Email senders should ensure that their recipient mailboxes are not spam trap addresses which can damage their reputation.
4. Disposable Email:
A disposable email address is a temporary email address used to protect the user's identity and privacy. It is a type of alias email address used for a specified period, after which the email address is permanently discarded and can no longer be used. These addresses are typically used for one-time or short-term activities such as registering on a website, sending a one-time message, signing up for a webinar or newsletter subscription, entering contests, or downloading freebies.
Typically, such an address will remain active for a limited period, after which the account and any messages sent to it will be deleted. Disposable email accounts provide an easy and secure way to protect users’ identities without the need to create a long-term account. It is an ideal solution for those who want to remain anonymous or protect their privacy when dealing with unfamiliar websites or services.
The main advantage of disposable email addresses is that it helps protect the user from spam, phishing, and other malicious activities. Disposable email addresses also help prevent the user's primary inbox from becoming exposed to potential scammers, advertisers, and other malicious actors. Furthermore, disposable email addresses can be used to test different services without signing up for the paid versions.
The use of disposable emails is becoming more commonplace as a way to thwart spam and other malicious activities.
5. Phishing:
Phishing using email is a type of cyber attack used by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, account numbers, Social Security numbers, and credit card information, by disguising as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication. Cybercriminals use this technique to send email messages that appear to come from reputable and legitimate sources, such as banks, financial institutions, government agencies, and other organizations, in an attempt to trick the receivers into releasing sensitive data.
Phishing emails are often sent out in the form of spam or bulk mail. They can also be sent out individually, which can be done either by sending an email with the recipient’s name in the “to” field or by sending an email that appears to come from someone they know.
Typically, these messages will ask recipients to click on a link or attachment in order to verify their identity or update their account information. However, the link or attachment actually directs the victim to a malicious website that appears legitimate but is actually a fraudulent website set up by the attacker where personal information can be stolen. Once the user enters the requested information, the attacker can use it to gain access to the victim’s accounts and sensitive data. Individuals need to be aware of the risks of phishing using email and how to recognize and avoid them.
6. Spoofing:
Spoofing in email is a technique used by fraudsters to disguise the origin of an email. This can be done by altering the email header, which usually contains the sender's address, to make it appear as if the message is from a legitimate source. It is the act of sending out emails with false sender information and usually a fake message. It is used to fool the recipient into taking action. Spoofing can be done by either hacking into someone's email account or by using a third-party service that allows you to send emails from any email address you want.
The most common type of spoofing is phishing, where the sender pretends to be a legitimate company in order to steal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers.
During spoofing, the malicious actor impersonates a legitimate sender in order to deceive recipients. These attackers use tools and techniques to manipulate the “From” field in order to make it appear as if the email originated from a trusted source. By doing this, attackers can gain access to confidential data, spread malicious software, or even commit financial fraud. Email spoofing is a serious threat, and individuals and organizations need to be aware and take steps to protect themselves from this type of attack.
To protect yourself from spoofing and phishing, it is essential to ensure that your email client is up to date with the latest security updates. Another way to do this is to ensure that all incoming emails are properly authenticated and have not been modified in transit. Organizations should also ensure that their anti-spam filters are up and running. Furthermore, always be cautious when opening emails from unfamiliar sources and do not click on any embedded links or attachments.
7. Blacklisting:

Blacklisting is a form of cybersecurity used to protect networks and systems from malicious actors, such as cybercriminals, spammers, and hackers. It is a preventative measure used to identify and mitigate malicious activities and protect user data. Blacklisting entails filtering certain messages, emails, or websites from an email server or web server. This can be done as an act of censorship or to block spam emails and other unwanted messages.
- Email blacklisting is a type of spam blocking that blocks emails from a particular sender. This is typically done when a user receives excessive spam emails from the same sender.
- IP blacklisting is a method of preventing access to a website, network, or other resources by denying the source address from which requests originate. It is the act of blocking IP addresses on a firewall or router to prevent unauthorized access to network resources. This type of blacklisting is often used to prevent unauthorized Internet access by individuals outside the company's firewall or to block service-denial attacks.
- Domain blacklisting is the act of blocking access to a domain by denying requests originating from that domain.
In short, email, IP, and domain blacklisting is the process of preventing emails from reaching certain recipients. It is done by listing out IP addresses, email addresses, and/or domain names associated with spam, viruses, malicious activities, or other unethical practices. When a particular IP address, email address, or domain is blacklisted, it means that the associated online accounts have been identified as a threat to the network or system and are blocked from accessing certain services.
These blacklists are often maintained by third-party organizations and provide a reliable source for email administrators to check for known malicious entities. When an email address, IP address, or domain name is found on a blacklist, it is blocked from accessing the recipient. This allows email administrators to reduce the number of malicious emails reaching their inboxes and protect their users from any potential security risks. It is essential to ensure that you are not sending emails to blacklisted email accounts.
By blocking suspicious IP addresses, email addresses, or domains, blacklisting can help reduce the risk of malicious activities, such as phishing attacks, spam, and ransomware.
How to Validate an Email Address
Ever wanted to know if someone's email is valid? Well, the answer is in the article. Email validation is a process that verifies whether an email address is legitimate or not. Some companies have also started implementing mailbox verification during sign-ups, which can only be completed by clicking on a confirmation link that appears in your inbox after typing in the address. Automatic email validation software has also been developed to help validate emails in real-time, and there are many available online for free.
There are 3 ways in which an email address can be validated:
1) Automatic Email Validation: This process relies on email verification software that checks for common errors, such as domain name typos or letters' incorrect capitalization. It can be done by typing in the email address in the single email verifier, and it will return a response of "valid", "invalid", or "unknown". The process involves determining, in real time, how many characters long the email address is, automatically checking that the domain name exists and has not expired, has a valid MX record, is not blacklisted, and much more.
The automatic email verification service usually has a bulk email verifier as well, which is generally used for validating bulk lists used for sending email campaigns. By analyzing the email addresses for typos, syntax errors, and other irregularities, a validation tool can determine whether an email address is indeed valid or not. In addition to flagging invalid email addresses, the email checker can also help identify email addresses that belong to real and active users or those under the control of a real human.
2) Mailbox Verification: This process involves sending a message to the mailbox associated with the email address and waiting for a response before confirming the validity. The response could either be a delivery confirmation or a bounce notification with a bounce code.
3) Manual Validation: To validate an email address manually, you first need to check the basic syntax of the address. This involves ensuring that the address has an ‘@’ symbol as well as a valid domain name after the ‘@’ symbol. Additionally, you should check if the top-level domain is valid, as the email address needs to be correctly formatted. This is typically done using a regular expression (regex). Once you have verified the syntax of the email address, you can move on to the next step, which is to check if the address is valid, e.g., through mailbox verification.

Benefits of Validating Emails
Email validation helps to protect both the sender and the recipient from spammers and phishing. The following are some other benefits of email validation:
- Ensures a higher deliverability rate.
- Encourages better customer engagement.
- Eliminates bounces and reduces unsubscribes.
- By verifying the accuracy and authenticity of email addresses, businesses can ensure that the emails they send are being delivered to the intended recipient.
- This helps maintain a professional reputation and increases the chances of a successful marketing or engagement campaign and sales.
- Additionally, email validation can help to improve the accuracy of customer data, allowing businesses to segment their customers better and target their messages.
- Validation helps avoid costly marketing campaigns being sent to incorrect or invalid email addresses and reduces the risk of being labeled as spam.
Potential Risks of Not Validating Emails
When email campaigns are conducted, be it email marketing or cold emails, prospects' lists must be validated. This is due to the potential risks that can arise from not validating emails or sending emails to invalid email addresses. Failing to validate email addresses can have serious repercussions, as this can result in significant financial losses and reputational damage.
- Email sent to invalid addresses could lead to your emails being marked as spam, blocked by the ESP, or blacklisted. This would result in your emails being automatically flagged or deleted and a decrease in customer engagement.
- If an email is sent to an invalid address, it can cause a significant delay in communication and potentially decrease customer satisfaction.
- Additionally, sending emails to invalid addresses can damage your reputation as it can cause your emails to be viewed as untrustworthy or untargeted, resulting in a decline in customer loyalty and hurting your sales.
- Furthermore, sending emails to invalid addresses could result in a high bounce rate, which can negatively impact the sender's reputation and lead to a decrease in deliverability rates and potential blacklisting.
Strategies for Improving Email Handling & Validation
Implementing effective email validation practices is important to ensure your organization’s digital communications security. Here are some useful strategies for improving your email handling and validation practices:
Utilize a double opt-in system. A double opt-in system is a two-step email authentication process that requires a customer to confirm their email address twice before any communication is sent. This helps to ensure accuracy and reduces the risk of spam emails or messages being sent to the wrong recipient. It also prevents the user from entering emails that are invalid or non-existent.
Implement effective spam filters. Spam filters can be used to detect and block emails that contain questionable content or links. This can effectively prevent malicious actors from reaching your inbox or appearing to be legitimate prospects.
Another strategy includes automating the process with email validation services and providing mailbox verification options to customers who need them.
Another strategy includes using automatic validation instead of manual validation, which can be time-consuming and error-prone.
You can also set up a bounce-back system to confirm that the emails sent from your domain are legitimate.
Create a blacklist of known malicious email addresses. By blocking emails from known malicious senders, you can protect your system from receiving unwanted spam or sending to fraudsters.
You should also take the time to review messages regularly to ensure that any suspicious or potentially dangerous emails are flagged and blocked.
Lastly, you can also consider using third-party services to verify email addresses or your entire communication infrastructure and protect your system from security threats.
Some companies also use a combination of these strategies, depending on their needs and requirements.
Conclusion/Takeaway
Validating email addresses is essential for any business that communicates with customers or potential customers via email. It helps to ensure that the mail intended for a customer or partner reaches the correct recipient on time. For businesses, validating email addresses provides numerous benefits, including increased customer engagement, improved data accuracy, and increased security.
Validation can therefore be used to strengthen email deliverability and improve user experience. It is a vital component of any email marketing strategy, helping to ensure that messages reach the right people and are not blocked or sent to spam. When your emails reach the right prospects, the chances of making a sale increase; thus, email validation indirectly influences your ROI.
